Quality Game Localization in 8 Steps

The game industry is one of the biggest industries in the world, and it is growing by the day.
Localizing video games has been a big way of promoting the games to a global audience since language barriers prevent many people from enjoying games.
Let’s dive into what game localization is and how you can do it to achieve global outreach for games.
What is Game Localization?
Game localization is a multi-faceted process that involves more than just translating the text from one language to another. It's about adapting a video game for different regional markets, ensuring that it resonates culturally and linguistically with players from various backgrounds. This process includes translating in-game text, dialogues, and manuals but also extends to modifying art assets, adjusting gameplay elements, and even altering content to meet cultural norms and local regulations.
Localization vs. Translation

While often used interchangeably, localization and translation are distinct concepts in the world of gaming. Translation is a subset of localization. It's the direct conversion of text from one language to another. Localization, however, is a broader, more comprehensive process. It encompasses translation but also involves cultural adaptation. This can mean changing idioms, humor, and cultural references so they make sense to players in different regions. For instance, a game might replace a culturally specific joke or idiom with something more universally understandable, or that resonates with the local culture.
The Importance of Cultural Adaptation in Games
Cultural adaptation is a cornerstone of successful game localization.
Games are a medium of storytelling and entertainment, and their appeal often hinges on how well players can relate to the content. Cultural adaptation ensures that a game's narrative, humor, symbols, and references are appropriate and engaging for players from different cultural backgrounds. This can involve altering characters, scenarios, or visuals to avoid cultural insensitivity or misunderstanding.
For example, a game set in a specific historical context might need to adjust its portrayal of events or characters to be sensitive to the audience in a particular region. Similarly, certain symbols or gestures considered benign in one culture might be offensive in another. Neglecting these aspects can lead to a game being poorly received, or even boycotted, in certain markets.
In summary, video game localization goes beyond mere translation, requiring a nuanced understanding of cultural differences. It's a critical process that can dramatically impact a game's global success, making it not just comprehensible, but culturally relevant and engaging for diverse audiences worldwide. This cultural adaptation is not just a courtesy but a strategic business move, enabling games to cross borders and become global phenomena.
The Challenges of Game Localization

Language Barriers and Nuances
One of the primary challenges of game localization services is navigating the nuances of different languages. Literal translations often fail to convey the original meaning, humor, or emotion. Slang, idioms, and colloquial expressions can be particularly tricky, as they may not have direct equivalents in other languages. Moreover, the linguistic subtleties and context that give depth to narratives and characters can be lost if not carefully adapted.
Cultural Sensitivities and References
Games often contain cultural references, which may be irrelevant or insensitive in other cultures. Ensuring cultural sensitivity is key. This might involve altering or removing specific content that could be considered offensive in certain cultures. For instance, symbols, historical events, or religious references might need to be adjusted to avoid misunderstandings or controversies.
Technical Aspects: Text Space, Voiceovers, and Coding Challenges

Technical aspects pose significant challenges for game localization services. Different languages occupy different amounts of space on the screen, which can affect the game’s layout and design. For instance, German text is typically longer than English, requiring more space. Voiceovers need to be redone in each language, considering lip-syncing and the characters' cultural backgrounds. Coding also becomes complex, as developers must ensure the game supports various character sets and scripts, like Cyrillic or Kanji.
Censorship and Regulatory Compliance in Different Regions
Different regions have different standards and regulations regarding content. What is acceptable in one country may be censored in another. Navigating these regulatory landscapes is crucial. Games may need to be altered significantly to comply with local laws and cultural norms, such as removing violent content, changing the portrayal of relationships, or even altering gameplay mechanics.
Case Studies of Successful Video Game Localization
"The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt"
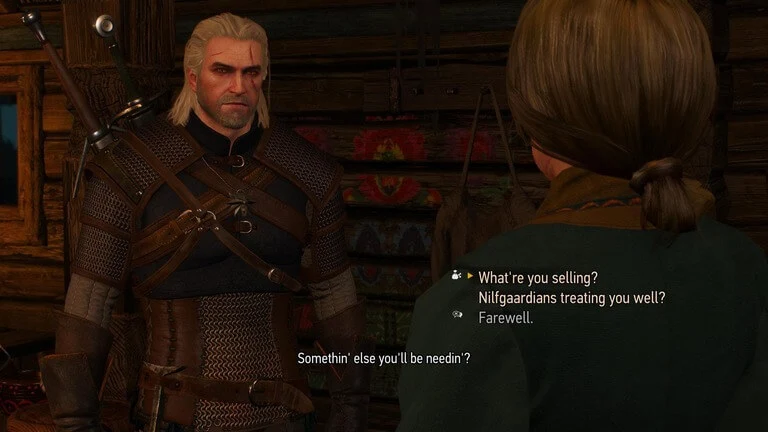

"The Witcher 3" is renowned for its exceptional localization. Despite its deeply rooted Slavic mythology, the game was successfully adapted for a global audience. This success can be attributed to the nuanced translation of the game’s rich narrative and dialogue, maintaining the original’s tone and cultural depth. The localization team also paid close attention to the voiceovers, ensuring that the characters' accents and dialects added to the immersive experience without alienating non-native players.
"Final Fantasy" Series
The "Final Fantasy" series is another excellent example of successful game localization. Each installment involves intricate world-building with unique cultures and languages. The localization team not only translated the text but also adapted the content to resonate with different audiences. This included altering certain character designs, dialogues, and cultural references to make them more relatable and appropriate for various regions. The series' ability to maintain narrative consistency and emotional depth across different cultures is a testament to its localization efforts.
Riot Games
Riot Games products are an incredible example of successful game localization because they are consistent in making their games accessible to an audience as wide as possible, and with quality video game localization. They hire the best talent out there for each language and try to translate the sentences as accurately as possible while maintaining cultural references with their counterparts in the target language, including some quotes in the original language to preserve authenticity.
Analysis of Success
These examples of successful localization share common elements. They involve early and comprehensive planning for localization, ensuring it is an integral part of the development process. The teams prioritized not just linguistic accuracy but also cultural relevance and sensitivity. Additionally, they invested in quality voice acting and careful adaptation of visual elements, contributing to a cohesive and immersive experience for players worldwide. This attention to detail in all aspects of localization is what sets these games apart and contributes to their global acclaim.
Step-by-Step Game Localization Strategy
Step 1: Understand Your Target Market
- Research: Before starting the localization process, it's crucial to understand the target audience. This includes cultural norms, preferences, and gaming habits.
- Identify Cultural Sensitivities: Be aware of cultural sensitivities and potential taboos in your target market to avoid any offensive content.
Step 2: Plan Your Localization Strategy
- Early Involvement: Involve your localization team early in the development process. This can help identify potential issues beforehand.
- Budget and Resources: Allocate a budget for localization and ensure you have the necessary resources, including skilled translators and localization software.
Step 3: Translation and Cultural Adaptation
- Hire Professional Translators: Use professional translators who are not only fluent in the target language but also understand the cultural context.
- Adapt Content: Modify content, including jokes, idioms, and cultural references, to make them relevant and respectful to the target culture.
Step 4: Localize Graphics and UI
- Adapt Visual Elements: Change graphics, symbols, and icons that may not be appropriate or relatable in the target culture.
- UI and Layout Adjustments: Adjust the user interface and layout to accommodate different text lengths and directions (like right-to-left scripts).
Step 5: Voice-Over and Audio Localization
- Casting Voice Actors: Choose voice actors who can accurately represent characters while considering the cultural background of the target market.
- Syncing Audio: Ensure that voice-overs are well-synced with characters’ lip movements and actions.
Step 6: Technical Localization
- Character Encoding: Ensure the game’s code can handle different character sets and text directions.
- Functionality Testing: Test the game to ensure all localized versions function correctly across different platforms and devices.
Step 7: Quality Assurance and Testing
- Cultural Testing: Have native speakers and cultural experts test the game to ensure cultural accuracy and relevance.
- Bug Fixing: Address any issues related to translation, functionality, or cultural adaptation.
Step 8: Marketing and Release
- Localized Marketing: Adapt your marketing materials to the target culture, including promotional texts, trailers, and social media content.
- Feedback and Updates: After release, monitor feedback from the localized markets to make necessary updates or improvements.
Game Localization with AI

Artificial intelligence is now at a point where translations of massive files are done within seconds, and with great accuracy.
Almost always, games have tons of text or audio in them because they consist of hours of content. Thus, localizing games with AI can be beneficial for everyone, even if you are certain about using professional translators.
Let’s say that the game is around 10 hours long with thousands of lines of text and dialogue. Translating that can take hundreds of hours, especially when you have to think about accurately localizing cultural references and nuances. But if you use an AI video translator, the same amount of translation work can be done in a fraction of the time, allowing you to polish and perfect the localization with all the time left in your hands.
An AI video translator can provide translation in multiple ways, such as subtitles or voiceovers. So, in essence, you can just upload a video of the game and export a full localization project, in as many languages as you want.
You can also use it as an accelerator and have it translate in bulk, so professional translators can focus on quality localization and creative translations.
The Future of Game Localization
Predictions for the Future of Game Localization

As the global gaming market continues to expand, the future of game localization is poised to evolve in significant ways. One key prediction is the increased use of AI and machine learning in the localization process. These technologies are expected to streamline the translation of in-game text, making initial translations faster and more cost-effective. However, human oversight will remain crucial for handling cultural nuances and creative content.
Another prediction is the rise of cloud-based gaming platforms, which will likely demand even more efficient localization processes. As games become more accessible globally through these platforms, the need for rapid and effective localization will increase. This might lead to the development of more sophisticated tools and software to manage large-scale localization projects seamlessly.
We can also anticipate a greater emphasis on inclusivity and representation in game content. This means localization teams will not only adapt content for different cultures but also ensure that games are sensitive to a wider range of social and cultural perspectives.
The Growing Importance of Localization in a Global Market
Localization is becoming increasingly important in the global gaming market for several reasons. First, the market itself is becoming more diverse, with emerging gaming communities in regions like Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa. Catering to these diverse audiences requires a deeper understanding of local cultures, languages, and preferences.
Furthermore, localized games tend to perform better commercially. They resonate more with local audiences, leading to higher engagement, stronger loyalty, and increased sales. As a result, game developers are recognizing localization as not just an optional add-on but a crucial part of their development and marketing strategy.
Potential Changes and Innovations in the Field

In terms of innovations, we can expect more immersive and sophisticated localization techniques. For instance, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) present new challenges and opportunities for localization. Localizing these experiences will involve not just text and audio but also the adaptation of entire virtual environments to different cultural contexts.
Another potential change is the increased collaboration between developers and localization teams from the earliest stages of game development. This approach ensures that games are designed with localization in mind, reducing the need for major changes later in the process.
Lastly, we may see a rise in community-driven localization, where gamers themselves contribute to the localization process. This approach can harness the power of the gaming community to create more authentic and diverse localizations.
In conclusion, the future of video game localization is dynamic and promising. With technological advancements, a growing global market, and a shift towards more inclusive content, localization will continue to play a vital role in the success of games worldwide. This evolution will not only enhance the gaming experience for players across different cultures but also open up new horizons for developers to explore and innovate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is localization of a game?
Localization of a game roughly means translating the game’s content in an appropriate manner by preserving cultural references through creative translation, without disrupting or removing the original meanings and richness of the content in the original language.
What are the top 10 languages for game localization?
English takes the lead if your game is in another language. Otherwise, French, Spanish, German, Hindu, Chinese, Turkish, Korean, Japanese, Italian and Polish are great languages for game localization in terms of ROI (return of investment) and outreach.
How do I localize my game?
You can localize games by hiring professional localization companies to localize the game for you. Or, you can utilize an AI translation tool to localize games in a cost-efficient and effective manner.
How much do game localizers make?
Game localizers can make between 25,000 and 45,000 USD annually, depending on their experience, expertise, and the languages they speak.
