Transcribing Interviews for Qualitative Research: Best Practices

The long hours dedicated to transcribing interviews are now in a galaxy far far away, thanks to the developments in AI and machine learning. Qualitative research highly benefits from these advancements as AI transcription technology not only saves valuable time but also increases research efficiency and accuracy.
In this blog, we emphasize the significance of transcribing interviews for qualitative research as well as the best practices in this area. We also explain why automatic transcription offers more advantages to researchers and how to choose an interview transcription software to achieve optimal results.
Let’s begin.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a systematic approach to understanding and explaining social phenomena. Focused on “How?” and “Why?” questions, it is an umbrella concept that involves different research methodologies including interviews, participant observation, focus groups and so on.

Qualitative data is based on words, behaviors and images. By analyzing these, qualitative research generates theories and hypotheses on how the social world is experienced and understood by people in everyday life. Unlike quantitative research that depends on numbers and statistics, qualitative research seeks to uncover the underlying meanings in human experiences.
Importance of Transcribing Interviews in Qualitative Research
Transcribing interviews for qualitative research offers several benefits that contribute to the overall depth and success of the research process. Here are its key advantages:
- Comprehensive analysis: Transcripts capture every word, nuance and non-verbal cue, which is a goldmine for data analysis. This allows researchers to identify themes and patterns thoroughly to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Enhanced reliability: Having the transcript for an interview will strengthen research validity by providing evidence to your argument. Plus, other researchers can review the transcription, ensuring transparency and collaboration.
- Reduced bias: Transcribing interviews will reduce bias as it minimizes the risk of misinterpreting or omitting information. Compared to note-taking, which may be influenced by the researcher’s perceptions, transcription offers a more objective representation of data.
- Increased accessibility: Via transcription, researchers can share and discuss findings with people who couldn’t participate in the interview due to language barriers. Furthermore, the practice improves accessibility for deaf and hard of hearing individuals by allowing them to engage with the findings through written text.
- Time-efficiency: No more jumping back and forth in audio files! When you transcribe the interview, you can quickly search for and navigate to specific parts, saving time during the analysis phase.
4 Types of Transcription
Transcription can be grouped into four categories: verbatim, intelligent verbatim, edited and phonetic. Let’s take a look at each one’s pros and cons, and highlight the best choice for transcribing interviews for qualitative research.
Verbatim Transcription
Verbatim transcription includes every sound in the audio recording such as coughs, doorbells and hesitations (er, mm, etc.) between sentences.
Pros: Provides the most complete and accurate record of the interview, which is essential for capturing the full context and subtle nuances.
Cons: May include unnecessary details. Can be time consuming and expensive to produce in case of manual transcription.
Primarily used in: legal proceedings, sociolinguistic research studies
Intelligent Verbatim Transcription
An intelligent verbatim transcript removes filler words and repetitions but retains key content and non-verbal cues. Its purpose is to provide a more on-point transcript.
Pros: Offers a balance between readability and details.
Cons: May sacrifice some context and require careful quality control to guarantee accuracy.
Primarily used in: qualitative research, especially in interviews and focus groups

Edited Transcription
Clarity is the main focus of an edited transcript. It corrects grammatical errors and eliminates filler words, repetitions and extraneous sounds.
Pros: More readable and concise, therefore suitable for general understanding and thematic analysis.
Cons: Risks losing some nuances and the authenticity of participants’ expressions.
Primarily used in: journalism and media contexts
Phonetic Transcription
Phonetic transcription is unorthodox as it uses symbols from the International Phonetic Association to represent sounds exactly as they are spoken. This includes accents, dialects and non-standard pronunciations.
Pros: Analyzing variations in pronunciation.
Cons: More complex and expensive than other types of transcription.
Primarily used in: linguistic studies
What is the best type for interview transcripts in qualitative research? As we’ve said above, intelligent verbatim transcription is often the best choice: It is readable and manageable for analysis, yet it also provides a detailed record of the conversation.
Still, always consider your research goals, questions, data and budget when transcribing interviews. An edited transcript might be sufficient if you want to focus on broader themes. Meanwhile, verbatim transcription can be pretty useful if details matter to you a lot.
Methods of Transcribing Interviews
There are two main methods when it comes to transcribing interviews: manual and automatic. While manual transcription involves a human transcriber typing out the spoken words in the interview, automatic transcription utilizes speech recognition technology to convert audio to text.
As in types of transcription, these two methods have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Human transcribers can better understand nuances and context. However, this method can also be pretty time consuming and it may be expensive to hire a professional transcriber.
On the other hand, automatic transcription is much faster and cost-effective. This is an important advantage in the realm of qualitative research where large amounts of interview data need to be processed and analyzed. You can definitely save time and resources by using software when transcribing interviews for research.
Moreover, automatic transcription services are getting more accurate day by day thanks to the developments in AI, machine learning and voice recognition. Current systems can handle diverse accents, linguistic variations and even contextual nuances very well. This significantly increases the reliability of the interview transcript and research results.
How to Choose an Interview Transcription Software
Decided to use an interview transcription software for research but confused on how to choose one? Look for these qualities when making your decision:
Accuracy
Accuracy is crucial when transcribing interviews as it directly influences the reliability of your data. Prioritize an AI-powered tool with a high accuracy rate to remain true to your original interview. We recommend you test the AI transcription software beforehand with a small sample of your interview.
Speed
Quick turnaround time is essential for researchers who work with large sums of interview data and tight deadlines. The right software must transcribe audio to text rapidly without compromising accuracy and meet the demands of an intense qualitative research process.
Security
It is your responsibility to comply with ethical standards and protect your participants’ sensitive information. You must choose a tool that has end-to-end encryption and clear privacy policies.

Flexibility
Does the transcription software allow you to upload audio and video files in different formats? Is it easy to edit the transcript and add notes? This flexibility will help you refine interviews seamlessly, enhancing the quality of your data.
Customization
Speaker identification, timestamps and punctuation are indispensable when transcribing interviews for qualitative research. Select a software that allows you to tailor these elements to your needs.
Language Support
Make sure that the tool supports the languages spoken in your interviews. Break down the language barrier by choosing a software that transcribes multiple languages and enrich your research with global perspectives.
Transcribing Interviews with Maestra Step-by-Step
If you’re looking for a tool with all these features, then Maestra’s AI-powered interview transcription software is the right choice for you. You can get your transcript instantly by following a few simple steps.
- Upload your audio or video file. Maestra supports 125+ languages.
- Select audio language and receive the transcript in seconds.
Custom dictionary is especially beneficial when transcribing interviews for research as the audio content is more likely to include technical terminology. With this feature, you can add specific terms to your custom dictionary, assign importance values and Maestra will transcribe them as specified, ensuring accuracy.
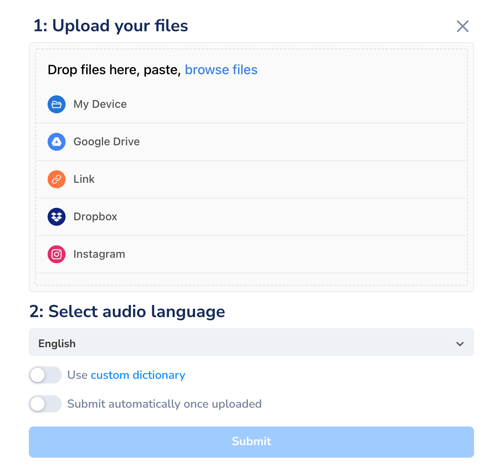
You can also select the number of speakers during the upload phase and assign names to each speaker, making it easier to navigate the transcript.
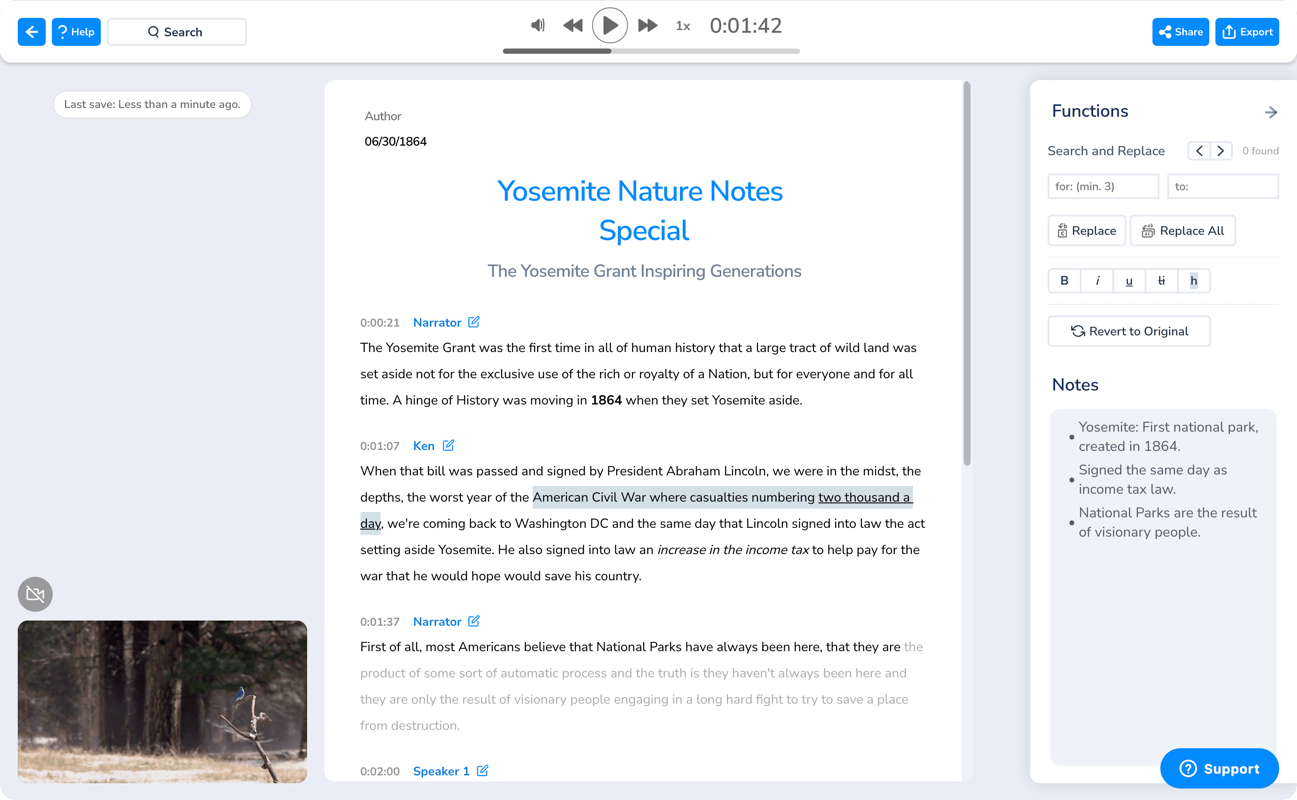
- Click “Submit” and witness AI transcription work its magic. You will instantly receive your interview transcript with timestamps and speaker tags.
- Ta-da! You can now proofread and edit your transcript, take notes and add comments with Maestra’s built-in text editor.
Maestra has a very high accuracy rate but you can always polish your document for maximum clarity and comprehensibility.
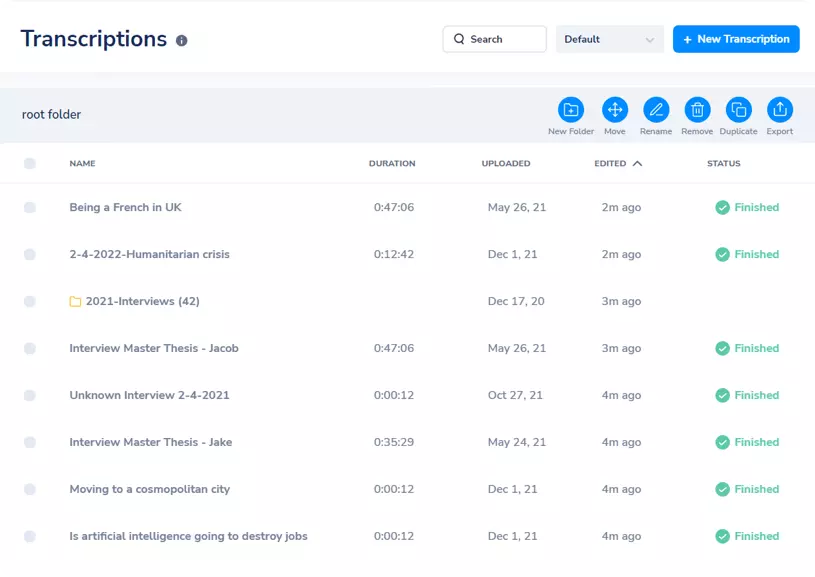
After transcribing interviews, you can safely reach and organize them via MaestraCloud. You can also store your interview recordings here as the cloud allows you to keep audio and video files of any size without time limitations.
Collaborating with fellow researchers? Maestra Teams is ready to help you. You can create team-based channels with different permission levels and edit the document with other researchers in real-time.
Tips for Transcribing Interviews for Qualitative Research
No matter your experience in qualitative research or the software you use, there are certain practices to adopt when transcribing interviews.
Use a High-Quality Recording Device
Utilizing a high-quality recording device lays a solid foundation for interview transcription. Invest in a reliable recorder with good microphone sensitivity and audio quality to capture every part of the conversation. Don’t forget to test your equipment beforehand to avoid potential technical issues during the interview.
Respect Confidentiality
Upholding confidentiality is paramount when transcribing interviews for qualitative research. Always obtain informed consent from participants for recording and transcription, and store your files securely. Avoid sharing any personally identifiable information to safeguard participant privacy and maintain the integrity of your research.
Include Speaker Identification and Time Stamps
This practice enhances the overall usability of an interview transcript by enabling easy reference to specific points. Make sure you clearly identify each speaker on the document either by name, role or pseudonym. You can use different fonts or colors to visually distinguish between speakers.

Follow the Specific Style Consistently
Choose a transcription style guide (verbatim, intelligent verbatim, etc.) and follow it consistently throughout the project. Define rules for punctuation, contractions and interruptions. This will guarantee uniformity and enhance the reliability of your findings.
Add Non-Verbal Cues and Annotations
This one is not mandatory but can provide valuable context. You can document non-verbal expressions, pauses or changes in tone to add depth to qualitative data analysis. Meanwhile, bracketed annotations can help you highlight important moments. Just remember that adding too much detail can be distracting, so only include relevant information.
Edit and Proofread the Transcript
Proofread and edit your document once transcribing an interview: correct any errors, format inconsistencies and review for readability. Double check speaker identification and timestamps for accuracy. These practices will ensure a smooth transition from transcription to analysis and publication.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is transcription necessary for qualitative research?
The necessity of transcription depends on the nature and goals of the qualitative research you conduct. For example, it is crucial for in-depth and focus group interviews but not essential for participant observation where researchers can rely on field notes.
How do you transcribe an anonymous interview?
When transcribing interviews with anonymous participants, remove any information that can directly or indirectly identify the participant such as name, nickname, location, job title and affiliations. Create neutral pseudonyms (Participant 1, Interviewee A, etc.) for the participant and use them consistently throughout the interview transcript.
How do you analyze interview transcripts in qualitative research?
First, familiarize yourself with the data through readings when analyzing an interview transcript for research. Then, assign codes to relevant segments and organize similar codes into broader recurring themes. Finally, present your findings via a structured narrative. Always maintain transparency during the process.
How do you transcribe an interview in APA format?
Transcripts of interviews are usually added to the appendix in APA format. You should use a specific header with interview details, double line spacing and speaker identifiers in the transcript.
How do you summarize an interview transcript?
Carefully read the content and identify key themes when summarizing the transcript of an interview. Organize the information logically, provide brief contextual details when necessary and use quotes to add impact. Capture the essence of the interview by keeping the summary short and sweet.
Summary
Interview transcription is particularly valuable in qualitative research, which delves deep into human experiences and perceptions. Transforming spoken words into text enables researchers to derive meaningful insights from the rich tapestry of qualitative data. It also increases the accessibility of the research, empowering scholars to collaborate with colleagues across disciplines and borders.
The advent of AI technology revolutionized the process of transcribing interviews and will continue to do so in the future. Its benefits range from increased accuracy to cost-effectiveness, providing a much refined experience for researchers. By choosing the right software and adopting the best practices for transcribing interviews, researchers can unleash the full potential of their endeavors.
