Audio Translation: Everything You Need to Know

Audio is the heartbeat of digital communication. Whether it’s a training video, a podcast, a product demo, a live webinar, or even a help desk call, audio lets us convey tone, nuance, and urgency that plain text simply can’t. But here’s the thing: if your message only speaks one language, it only reaches one audience.
That’s where audio translation comes in.
Until recently, audio translation was slow, expensive, and limited to enterprises with localization budgets. Today, thanks to AI, it’s fast, affordable, and scalable. Tools like Maestra make it possible to translate spoken content into 125+ languages, with just a few clicks. And that opens the door to new viewers, markets, learners, customers, and communities around the world.
In this guide, we’ll unpack everything you need to know: what audio translation is, why it matters, the tools that power it, how to use it, and best practices to avoid the most common pitfalls. Whether you’re a creator, educator, business, or nonprofit, this guide will show you how to make your voice truly global.
What Is Audio Translation?
%20(3).webp)
At its core, audio translation is the process of taking spoken content in one language and converting it into another language.
While that sounds simple, under the hood it usually involves three main steps:
- Transcription
The original audio is converted to text. This can be done manually or with AI speech recognition. - Translation
The transcript is then translated into the target language using machine translation tools or human translators. - Audio Rendering (optional)
The translated text is turned back into audio using text-to-speech (TTS) engines or voice actors, often AI-generated voices today.
Depending on the context, audio translation can take different forms:
- Real-time translation (live meetings, events)
- Post-recorded translation (videos, podcasts, courses)
- Subtitling and captioning
- Full dubbing with voice cloning
The result: people can hear your message in their own language, whether they’re watching a livestream, tuning into a podcast, or learning from a training video.
Try an AI Audio Translator
Why Audio Translation Matters in 2025
Audio translation is no longer a nice-to-have. In 2025, it’s becoming a standard, expected by users, enforced by compliance rules, and essential for anyone trying to grow across borders. Here’s why.
1. Multilingual Audiences Are the Norm

Let’s start with the numbers:
- There are over 5.4 billion internet users in 2025.
- Only 17% of them speak English as a first language.
- Over 76% prefer to consume content in their native language, even if they understand English.
In other words, speaking only one language online is like putting up a “closed” sign for three-quarters of your potential audience.
Whether you're a solo creator or a multinational company, your users are multilingual and they expect your content to be too.
2. It Makes Content Discoverable
Translated audio improves your visibility across the board:
YouTube: Multilingual subtitles and dubbed audio improve watch time, engagement, and international search visibility.
Podcasts: Translating episodes increases your reach in non-English-speaking markets.
Websites: Audio + transcript translations boost SEO rankings for foreign-language keywords.
Livestreams: Offering real-time interpretation reduces bounce rates and increases participation. Find out how you can translate live streams in real-time.
Translation doesn’t just help users understand. It helps them find you in the first place.
3. It’s a Shortcut to Accessibility and Inclusion

Translation overlaps with accessibility in powerful ways:
Subtitles and transcripts help users who are deaf or hard of hearing.
Real-time captioning helps neurodivergent users process speech more effectively.
Multilingual support makes information more equitable in global communities.
Audio translation also helps meet standards like:
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act)
- WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Accessible content is more inclusive, more compliant, and more human-friendly.
4. Compliance Isn’t Optional
Depending on your industry, translating your audio content may not just be a best practice, it might be a legal requirement.
For example:
- Education platforms must often support multiple languages and captioning.
- Public sector content may need to be published in multiple official languages.
- Corporate training materials in multinational companies require localization to avoid liability and miscommunication.
If you’re working across borders, investing in audio translation isn’t just smart, it’s safe.
5. It Drives Revenue and Retention
According to CSA Research:
- 72% of consumers are more likely to purchase a product if the info is in their language.
- 55% will only buy from websites that offer information in their language.
People don’t just want translation, they expect it. And when they get it, they’re more likely to convert.
Audio translation also increases:
- Video watch time
- Podcast completion rates
- Course retention
- Onboarding effectiveness
It’s not just about reach. It’s about resonance.
6. It Empowers Creators and Small Teams

Five years ago, you needed a localization department to create content in multiple languages. Now? A creator with a laptop and a tool like Maestra can dub their YouTube series in Spanish, add subtitles in French, and push a course in Hindi, without hiring a team.
AI-powered tools democratize translation. They put international reach within reach.
7. It Speeds Up Internal Communication
Audio translation is a powerful asset for internal operations, especially for global or remote teams. Use it to:
- Translate recorded meetings for cross-border collaboration
- Localize training videos for new hires
- Document compliance and safety messages in every team’s language
When everyone understands the message, everything moves faster.
Types of Audio Translation (And When to Use Each)
Audio translation isn’t one-size-fits-all. Depending on your content, timeline, and audience expectations, different formats may be better suited to your goals. Below are the four main types, and when to use them.
1. Real-Time Audio Translation
.webp)
What it is:
This method translates spoken language as it's happening, either as text (captions) or speech (interpreted audio). Powered by low-latency AI and speech recognition, it's commonly used in:
- Live webinars and broadcasts
- Zoom or Meet calls with multilingual participants
- Global team meetings and training sessions
- Virtual events and conferences
Pros:
- Instant access for global participants
- No need for human interpreters
- Ideal for live communication (through real-time translation)
Cons:
- May struggle with strong accents, poor audio, or overlapping speech
- Slight delay may occur in speech output
Who it's for:
Brands hosting live launches, educators teaching global classrooms, or any team wanting real-time collaboration without a shared native language.
2. Post-Recorded Audio Translation
What it is:
Pre-recorded content is translated after recording. You upload a video or audio file, and it’s processed into a new version with translated text and/or dubbed audio.
Best used for:
- YouTube videos
- Podcasts
- Training videos
- Explainers and product demos
- E-learning content
Pros:
- Greater accuracy and polish
- Can review and edit before publishing
- Options for dubbing, subtitles, and voice cloning
Cons:
- Not suitable for live interaction
- Slightly longer turnaround (though often still fast with AI)
Who it's for:
Anyone distributing polished content in multiple markets, especially marketers, educators, and course creators.
3. Subtitle-Based Translation
What it is:
Instead of redubbing audio, you simply generate translated subtitles. These appear as on-screen captions synced with the original audio.
Use cases:
- Social videos
- Online courses
- Documentaries
- Corporate training
Pros:
- Easy to distribute across platforms
- Viewers can choose to toggle subtitles
- Low production cost
Cons:
- Reading subtitles while listening may not suit all viewers
- Requires accurate timing for best experience
Good to know:
Tools like Maestra auto-sync subtitle files and let you export in SRT, VTT, and SBV formats, compatible with YouTube, Vimeo, and more.
4. Voice Cloning & AI Dubbing
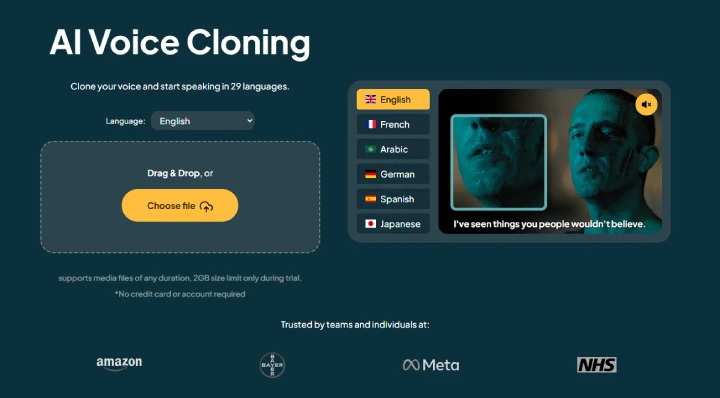
What it is:
AI replicates the speaker’s voice and renders the translated speech in the same tone, rhythm, and cadence as the original, just in another language.
Why it matters:
- Keeps content personal and brand-consistent
- Builds trust through voice familiarity
- Great for creators who are “the face” of their content
Who uses it:
- Influencers
- Course instructors
- CEOs in corporate messaging
- Brand narrators and spokespeople
Using Maestra (one of the best voice cloning software out there), you can generate dubbed audio with cloned voices in minutes, and make it sound like you never switched languages.
How Audio Translation Works: Step-by-Step
Let’s walk through the process from start to finish. Whether you're translating a 2-minute pitch or a 90-minute masterclass, the workflow is largely the same:
Step 1: Upload Your Content
Most audio translation tools support a wide range of formats:
- Audio files: MP3, WAV, M4A
- Video files: MP4, MOV, AVI
- Links: YouTube, Vimeo, Dropbox
- Direct microphone input (for real-time capture)
Uploading is typically drag-and-drop. No need for file conversions or tech skills.
Step 2: Transcription (Speech-to-Text)
%20(2).webp)
The platform listens to your file and transcribes what’s being said using automatic speech recognition (ASR). This generates a time-synced transcript with speaker labels and punctuation.
Tip: Clean audio equals better transcription. Avoid background noise and use a decent mic for best results. Here is a list of the best live transcription apps.
Step 3: Translation
The transcript is run through a machine translation engine that converts the content into your selected target language(s). Tools like Maestra support over 125 languages, including:
- Spanish
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Hindi
- Arabic
- Japanese
- Korean
- Turkish
- Russian
You can choose multiple outputs at once, great for global rollouts.
Step 4: Voice Synthesis (Optional)
If you want a dubbed audio version, you can now choose a voice:
- Generic voices: Male/female options in different accents
- Voice cloning: Upload samples of your own voice for personalized dubbing
- Tone matching: Adjust pace and inflection for more natural results
The platform then renders a fully translated voiceover that syncs with the original video.
Step 5: Review and Edit
Good tools will let you:
- Correct transcripts
- Adjust subtitle timing
- Replace words or phrases
- Choose different voices or accents
- Add or remove pauses for pacing
This is where you polish the output before publishing.
Step 6: Export or Publish
Once finalized, you can:
- Export subtitle files (SRT, VTT, etc.)
- Download translated audio files
- Get dubbed video versions with synced voiceover
- Share directly to platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, or learning management systems
Maestra’s dashboard lets you manage all your multilingual content in one place, project by project, file by file.
📦 Real-world example:
A YouTube educator uploads a 15-minute tutorial. Maestra:
- Generates a transcript in 90 seconds
- Translates it into 4 languages
- Dubs each version in her cloned voice
- Delivers all assets (video, subtitles, and audio tracks) within 10 minutes
She’s now reaching new viewers in Brazil, Turkey, and India, without rerecording a thing.
Best Tools for Audio Translation
The quality of your audio translation is only as good as the tools you use. Below is an in-depth look at the leading platforms in 2025 for creators, educators, businesses, and developers alike. We’ll break them down by use case, capabilities, pros, cons, and ideal users, so you can make the best choice for your workflow.
🔹 1. Maestra AI
.webp)
Who it's for:
Podcasters, video creators, YouTubers, course creators, educators, marketing teams, enterprise L&D departments, and anyone seeking an end-to-end solution.
Key Features:
- Live and on-demand audio translation
- AI-powered audio translator with advanced features
- Voice cloning and AI dubbing with tone/pacing control
- Real-time voice translation and voice cloning (Zoom, Meet, Livestream)
- Export to MP3, MP4, SRT, VTT, and direct platform publishing
- Team-friendly dashboard with collaboration tools
What makes it stand out:
Maestra isn’t just an audio translator; it’s a full platform for multilingual content production. Its voice cloning feature helps maintain brand consistency, while real-time options make it ideal for teams running international events.
Pros:
✔️ Plug-and-play simplicity
✔️ Clean UI, no tech skills needed
✔️ Scales for solo creators and teams
✔️ High voice quality in dubbing
✔️ Subtitles and audio exported in multiple formats
Cons:
❌ Limited editing for multi-layer videos (e.g., graphics/text baked into frames)
❌ Subscription required for advanced uses
Best for:
Creators and organizations who want speed and quality without needing complex post-production pipelines.
🔹 2. Descript + DeepL
Who it's for:
Experienced content creators, video editors, and podcast producers who want control over every layer of translation, editing, and publishing.
Descript Features:
- Podcast and video editing with text-based control
- Overdub feature for simple voice cloning
- Transcription and timeline-based edits
- Multi-track audio editing
DeepL Features:
- One of the most accurate translation engines for European and Asian languages
- Better contextual understanding than Google Translate
- API for programmatic integration
Workflow:
Use Descript to transcribe and edit, then export the script into DeepL for translation. Re-import translations into Descript for subtitling or dubbing.
Pros:
✔️ Fine-grain creative control
✔️ Works well with high-production value projects
✔️ DeepL provides advanced translation nuance
Cons:
❌ No real-time functionality
❌ Manual workflow adds time
❌ Voice cloning is less natural than Maestra’s
Best for:
Teams creating documentaries, branded podcasts, or educational series with creative production needs.
🔹 3. YouTube Studio + Google Translate
Who it's for:
Beginner YouTubers and casual content creators who need free tools for subtitle translation and basic accessibility.
Features:
- Auto-captioning in multiple languages
- Manual caption editing in YouTube Studio
- Google Translate for quick translation (not always contextually accurate)
- Community-submitted translations (if enabled)
Pros:
✔️ Completely free
✔️ Built directly into YouTube
✔️ Decent for English + 1 target language
Cons:
❌ No voice dubbing
❌ Inconsistent translations for complex sentences
❌ Limited export functionality
Best for:
Creators who need to localize a few videos without investing in premium tools or workflows.
🔹 4. Kapwing
Who it's for:
Social media marketers, short-form content creators, and video editors who need subtitles and basic translations built into their editing suite.
Features:
- Auto-captioning for video content
- Subtitle styling and animations
- Basic translation into 70+ languages
- Online video editor with built-in effects
Pros:
✔️ Easy for Instagram Reels, TikTok, and short YouTube videos
✔️ No software installation
✔️ Quick editing + publishing
Cons:
❌ Translation accuracy varies
❌ No voice dubbing
❌ Not ideal for long-form content
Best for:
Agencies and creators posting multi-language short-form content frequently.
🔹 5. Whisper by OpenAI
Who it's for:
Developers building custom audio translation pipelines, AI researchers, and advanced teams embedding translation features into products.
Features:
- Open-source speech-to-text model
- High accuracy on noisy or low-quality audio
- Strong multilingual recognition
Pros:
✔️ Developer-friendly
✔️ Customizable
✔️ Robust for experimental or academic use
Cons:
❌ No GUI or turnkey interface
❌ Requires integration with translation APIs and TTS separately
❌ Not suitable for non-technical users
Best for:
Engineering teams building proprietary translation tools into apps, products, or internal workflows.
Bonus Mentions:
- VEED.io: Online video editor with auto-translate and subtitle generation
- Sonix.ai: Great for transcription and translation with speaker separation
- Lumen5: Not strictly a translation tool, but supports multilingual video creation for marketing teams
✅ Summary Table
| Tool | Best For | Dubbing | Subtitles | Real-Time | Voice Cloning | Ease of Use |
| Maestra | Creators, teams, educators | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Descript + DeepL | Editors, professionals | ✅ Yes* | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Limited | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| YouTube + GT | Beginners, casual creators | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Kapwing | Social creators, marketers | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Whisper (OpenAI) | Developers, researchers | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ❌ No | ⭐⭐ |
Expert Tips for Better Audio Translation
Whether you're using Maestra or stitching together your own workflow, these best practices will help you avoid costly mistakes and create professional-grade multilingual content.
1. Use Clean, High-Quality Audio
Poor input = poor output. Make sure your audio:
- Has minimal background noise
- Is spoken clearly and at a natural pace
- Doesn’t have overlapping voices unless necessary
If it’s hard for a human to understand, an AI will struggle too.
2. Avoid Idioms, Jargon, and Slang
Phrases like “let’s circle back” or “this is a slam dunk” don’t always translate cleanly.
If you do use them, either:
- Offer brief context in your script
- Review the translated output carefully for meaning
Clarity > cleverness when you're going global.
3. Keep Sentences Short and Structured
AI translation tools handle concise, well-structured speech more reliably. Avoid:
- Super long monologues
- Run-on sentences
- Jumping between unrelated topics mid-sentence
Pro tip: Write like you speak, clearly and with purpose.
4. Always Review Translations Manually
Even the best AI makes mistakes, especially with:
- Brand names
- Technical vocabulary
- Contextual nuance
Have a native speaker review your output if possible, especially for high-stakes content.
5. Choose the Right Output for Your Audience
Don’t assume everyone wants dubbed audio. In some cases, subtitles are more effective:
- If your users are in environments where they can’t play sound
- If your content is already fast-paced
- If you're translating for learning purposes
Offer both when in doubt.
Industries & Use Cases
Audio translation isn’t just for creators or corporations. It’s transforming communication across every sector, better every day through AI audio translation. Here’s how different industries are using it:
Education

- Translate course lectures into 10+ languages
- Offer dubbed video instructions for global students
- Localize onboarding for international cohorts
- Sync subtitles with LMS platforms
Impact: More inclusive, accessible learning.
Media & Entertainment
- Voiceover international trailers
- Subtitle viral content across platforms
- Clone podcast hosts’ voices in other languages
- Expand YouTube audiences without re-recording
Impact: More views, higher retention, stronger brand voice.
Marketing & Advertising
- Run multilingual campaigns from one video shoot
- Clone spokesperson voice for localized promos
- Increase ad performance with native-language voiceovers
Impact: Better ROI, faster deployment.
Corporate & Enterprise
- Translate meetings in real-time
- Localize HR and compliance training
- Onboard international employees without delays
- Create unified global messaging in dozens of languages
Impact: Less friction, more alignment.
Healthcare & Public Services
- Translate patient instructions and outreach campaigns
- Dub informational videos for multiple communities
- Ensure accurate communication in high-stakes settings
Impact: Saves lives, builds trust, improves compliance.
Nonprofits & NGOs
- Translate impact stories, grant applications, and fundraising videos
- Use the best voice translator apps to cross borders with a single campaign
- Support multilingual communities in real time
Impact: Greater reach, better community engagement.
6 High-Impact Ways to Expand Your Audio Translation Strategy
✅ 1. How Audio Translation Powers Global Learning

Why add this: Expand on education use cases with detail for LMS platforms, MOOC providers, and multilingual classrooms.
Key ideas:
- How AI translation apps improve course accessibility and learner retention
- Synchronous vs. asynchronous translation for education
- Integrating Maestra with Thinkific, Teachable, or Moodle
- Case example: international onboarding for corporate training
Estimated length: 500 words
✅ 2. Audio Translation for Podcasts: A Growth Strategy
Why add this: Podcasting is exploding globally, but audio localization is still underused. Position Maestra as the smart play.
Key ideas:
- Growing non-English podcast markets
- How to translate and dub entire podcast seasons
- Subtitle your podcast for YouTube Shorts and TikTok
- Best practices: avoid regional slang, offer transcripts
- Workflow: Maestra + hosting platforms (Spotify, Buzzsprout)
Estimated length: 500–600 words
✅ 3. How to Translate Audio for Compliance and Risk Reduction
Why add this: Speak to enterprise buyers and regulated industries.
Key ideas:
- Translating for GDPR, HIPAA, ADA, and WCAG
- Examples: medical training videos, legal instructions, safety onboarding
- Why subtitle + voice translation reduces legal ambiguity
- Version control and audit trails in multilingual content delivery
Estimated length: 400–500 words
✅ 4. Audio Translation in Customer Support
Why add this: Shows how translation improves CX, support deflection, and international help desk operations.
Key ideas:
- Auto-translating tutorial videos and help docs
- AI dubbing for FAQs, walkthroughs, IVR systems
- Impact on ticket resolution and NPS
- How to use translated support videos in chatbots and self-serve flows
Estimated length: 400 words
✅ 5. How to Build a Multilingual Content Strategy with Audio at the Core
Why add this: Speak to marketers, content ops, and SEO strategists.
Key ideas:
- Creating audio-first content, then translating
- Using audio for keyword localization
- Repackaging translated content for social, email, blog, landing pages
- Building multilingual topic clusters and linking them back to pillar pages
- Embedding localized audio in blog posts
Estimated length: 600–700 words
✅ 6. Roadmap: What’s Next for Audio Translation Technology
Why add this: Forward-looking, visionary content helps build authority.
Key ideas:
- Emotion-aware translation and prosody mapping
- Speaker diarization and tone matching
- AI dubbing with lip-sync
- Cross-lingual voice search
- Ethical AI and bias reduction in voice datasets
Estimated length: 500 words
🚀 Summary
| Section | Purpose | Est. Length |
| Global Learning | Use-case deep dive | 500 words |
| Podcast Growth | Trend + tools | 500–600 |
| Compliance | Enterprise appeal | 400–500 |
| Customer Support | Operational benefit | 400 |
| Content Strategy | SEO & growth play | 600–700 |
| Future of AI Audio | Thought leadership | 500 |
Localization vs. Translation vs. Dubbing
These three terms often get used interchangeably, but they mean different things. Understanding the difference can help you decide how to approach multilingual content the right way.
Translation
Definition: Converting words from one language into another while preserving the original meaning.
Example: Translating the phrase “Welcome to our course” from English to Spanish as “Bienvenidos a nuestro curso.”
When to use it:
- You need accuracy and clarity
- You’re creating transcripts, subtitles, or written documents
Check out the best translation apps to use right now.
Localization
Definition: Translation + cultural adaptation. This involves adjusting expressions, references, formatting, and tone to feel native to the target audience.
Example: Changing “football” to “soccer” for an American audience or adjusting currency, idioms, and even humor styles.
When to use it:
- You want to connect emotionally
- You’re entering a new market or launching a product
- You’re adapting marketing, education, or brand messaging
Dubbing
Definition: Replacing original spoken audio with translated audio, often synced with lip movements and intonation.
Example: Translating a training video into Portuguese and replacing the English narration with a new AI-generated Portuguese voice.
When to use it:
- You want a smooth, immersive experience
- You’re creating media for platforms like YouTube, e-learning, or advertising
- You want viewers to listen instead of read subtitles
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best tools, it’s easy to slip up. Here are some of the most common missteps (and how to avoid them).
1. Not Reviewing the AI Output
Even the best AI doesn’t understand context like a human. Always:
- Review translations
- Check subtitle timing
- Confirm tone and clarity
AI helps you go faster, not publish blindly.
2. Relying on Literal Translation
Direct translations often miss the mark. “Break a leg” in English becomes nonsense in other languages. Use context, simplify language, and aim for clarity, not poetry.
3. Skipping Voice or Accent Matching
If you’re dubbing, make sure the new voice matches your audience. A British-accented narrator in Japanese might sound jarring unless your audience expects it.
Choose tone, speed, and gender consciously.
4. Forgetting Accessibility Standards
Subtitles are important. Always include them, even if you’re dubbing. Some viewers prefer to read, others need captions to engage fully.
Export multiple formats (SRT, VTT) for flexibility.
5. Not Planning for Multilingual Publishing
If you’re translating content, consider where and how it will be used. Some platforms (like Instagram) don’t support subtitles. Others (like YouTube) allow multiple tracks. Match format to platform early in the process.
FAQs
How do I translate live audio?
To translate live audio, you need a platform that supports real-time speech recognition, instant translation, and live captioning or dubbing. Tools like Maestra Live Translation are specifically designed for this purpose.
Here’s how it typically works:
Capture the live audio from a microphone or streaming input (e.g., Zoom, Google Meet).
Transcribe the spoken content using automatic speech recognition (ASR).
Translate the text into your target language(s) using machine translation.
Display the translation as captions on screen or convert it into spoken audio using text-to-speech (TTS).
Some platforms can even translate into multiple languages simultaneously, letting participants choose their preferred language channel. Real-time translation is useful for international meetings, conferences, hybrid events, and livestreamed content.
Pro tip: For the best results, use a high-quality mic, avoid overlapping voices, and speak at a steady pace.
How do I translate text to audio?
To translate text to audio, you can follow a two-step process:
Translate the text using a machine translation engine (e.g., DeepL, Maestra, or Google Translate).
Synthesize the translated text into speech using a text-to-speech (TTS) tool.
Platforms like Maestra simplify this by combining both steps. You upload a script or transcript, choose a language, and select a voice (including cloned ones). The platform generates a translated audio file in a natural-sounding voice—ready to download or publish.
Use cases include:
Dubbing explainer videos
Narrating blog posts or e-books
Creating voiceovers for social content
Multilingual voice assistants and IVR systems
Advanced option: Use voice cloning to preserve your own voice across translations.
How to do Google Translate audio?
Google Translate supports basic audio translation, but it’s limited in scope compared to dedicated platforms like Maestra. Here’s how you can use it:
Open Google Translate on your browser or app.
Select your source and target languages.
Click the microphone icon to start speaking (on mobile only).
Google Translate will transcribe your voice and show the translation.
Click the speaker icon next to the translated text to hear it spoken aloud.
Limitations:
It’s not real-time for full conversations.
You can’t export audio files.
No voice customization or dubbing support.
It doesn’t support long recordings or live meetings.
Use it for: casual phrase translation or quick pronunciation checks.
Don’t use it for: professional voiceovers, media, or real-time events.
Can ChatGPT translate live audio?
No, ChatGPT (including GPT-4) cannot translate live audio directly. While it can handle text-based translation, it doesn't have built-in capabilities to:
Process live microphone input
Transcribe or recognize speech in real time
Convert text into audio with TTS
However, you can use ChatGPT as part of a manual workflow:
Transcribe speech using another tool (like Whisper or Maestra).
Paste the text into ChatGPT for translation.
Use a separate TTS service to generate audio.
If you're looking for real-time audio translation, ChatGPT is not the right tool. Use platforms like Maestra, Zoom Live Transcription, or Interprefy for live applications.
Can AI translate in real time?
Yes, and it’s getting incredibly good at it.
Real-time AI translation relies on three main technologies working in sync:
Speech recognition – turns audio into text
Machine translation – converts that text into another language
Speech synthesis (optional) – converts the translated text back into spoken audio
Platforms like Maestra, Microsoft Translator, and Zoom with interpretation use these systems to offer near-instant translation in live settings.
Modern AI systems can now:
Identify speakers (speaker diarization)
Maintain timing and tone
Handle domain-specific vocabulary with training
Translate in over 100 languages with <1 second delay
While not yet perfect, AI real-time translation is accurate enough for meetings, webinars, and public events—making human interpreters optional in many scenarios.
Is audio translation free with Maestra?
Yes, Maestra offers a free trial that gives you access to the platform’s core features, including:
Automatic transcription
Subtitle generation in multiple languages
Basic audio translation
Limited voice dubbing with preset voices
Downloadable subtitle files (SRT, VTT)
This allows you to test workflows like translating a short video, adding subtitles, or experimenting with different output formats—all without entering a credit card.
For heavier use, you can upgrade to paid plans which unlock:
Voice cloning (your own voice in multiple languages)
Real-time live translation during meetings or webinars
Multiple export formats including dubbed video
Team management tools for collaboration and version control
Longer upload durations and faster processing speeds
So yes, you can start translating audio for free, and scale as your needs grow.
Can I clone my voice across languages?
Yes, Maestra allows you to clone your voice using AI-powered voice modeling. This feature lets you record a few voice samples (or upload existing content), and the system will build a digital version of your voice that can:
Speak fluently in over 125+ languages
Match your tone, rhythm, and inflection
Adapt to different emotions and energy levels over time
Maintain consistency across dubbed videos, training, or social content
This is incredibly useful for:
YouTubers who want to stay on-brand without re-recording
Course creators localizing modules for different regions
Executives delivering messages to global teams
Podcasters expanding to non-English listeners
Voice cloning takes personalization to the next level—it’s not just translation, it’s multilingual authenticity.
Does it work for live meetings?
Absolutely. Maestra supports real-time audio translation and captioning, which means you can use it in:
Zoom calls
Google Meet and Microsoft Teams
Livestream events
Webinars
Town halls and global all-hands meetings
Here’s how it works:
You or a speaker talks as usual.
Maestra captures the audio and transcribes it in real-time.
The system translates that transcription into one or more languages.
Viewers can read translated captions or hear the interpreted version via synthetic speech.
This makes it ideal for global collaboration and accessibility, especially for distributed teams working across time zones and native languages.
You can also generate a recording after the meeting, complete with:
Translated subtitles
Full multilingual transcript
Downloadable dubbed audio versions
It turns every meeting into a multilingual asset.
How accurate is AI voice translation?
AI audio translation has made incredible strides in recent years. Maestra’s system uses state-of-the-art neural machine translation (NMT) combined with custom-trained speech recognition models, achieving over 90% accuracy for standard business, educational, and media content.
However, accuracy can vary depending on:
Audio quality (clear voices = better transcription)
Speaker accent or dialect
Use of technical or niche terminology
Background noise and overlapping voices
The complexity of sentence structure
For sensitive content—like legal contracts, compliance training, or high-level negotiation—it's a good idea to review translations manually or bring in native-language editors for QA.
Maestra makes that easy by letting you edit directly in the platform before exporting or publishing.
What audio formats are supported?
Maestra is built for flexibility. Whether you’re working with audio-only content, full videos, or just want subtitle files, the platform supports a wide range of file types:
Audio Input:
MP3
WAV
M4A
AAC
Video Input:
MP4
MOV
AVI
WebM
Subtitles & Transcripts:
SRT (SubRip Subtitle)
VTT (Web Video Text Tracks)
SBV (SubViewer)
TXT or PDF (for transcripts)
Export Formats:
Dubbed audio (MP3 or WAV)
Translated video (MP4 with embedded subtitles or voiceover)
Separate subtitle files for YouTube, Vimeo, LMS platforms
Text transcripts in multiple languages
This makes Maestra compatible with most content platforms, including YouTube, Vimeo, Teachable, Thinkific, Kajabi, WordPress, and even offline playback systems.
Do I need to be tech-savvy to use an audio translator?
Not at all. Maestra was built for non-technical users, including marketers, teachers, small business owners, and creators.
You don’t need:
Editing software
Audio engineering knowledge
Coding skills
Voice acting experience
Everything works in your browser through a drag-and-drop interface. Once your file is uploaded, the platform guides you through each step—transcription, translation, dubbing, editing, and export—with clear prompts and previews.
Even advanced features like voice cloning or team collaboration are easy to use. And if you get stuck, support resources and tutorials are built in.
It’s like having a full localization studio in your browser, minus the complexity.
Start Translating Today
Audio translation is the fastest way to scale your voice across borders. Whether you’re educating, entertaining, informing, or selling, your content deserves to be heard, in every language.
With Maestra, it’s easy. Upload a file, pick your languages, and let the AI handle the heavy lifting.
- Speak to audiences in 125+ languages
- Clone your voice and maintain brand tone
- Create subtitles, dubbed audio, or both
- Translate live meetings or recorded assets
- No special tools or skills needed
No credit card required.
No need to re-record.
Just real, fast, multilingual content.
👉 Try Maestra’s Audio Translator
